What is a UTI?
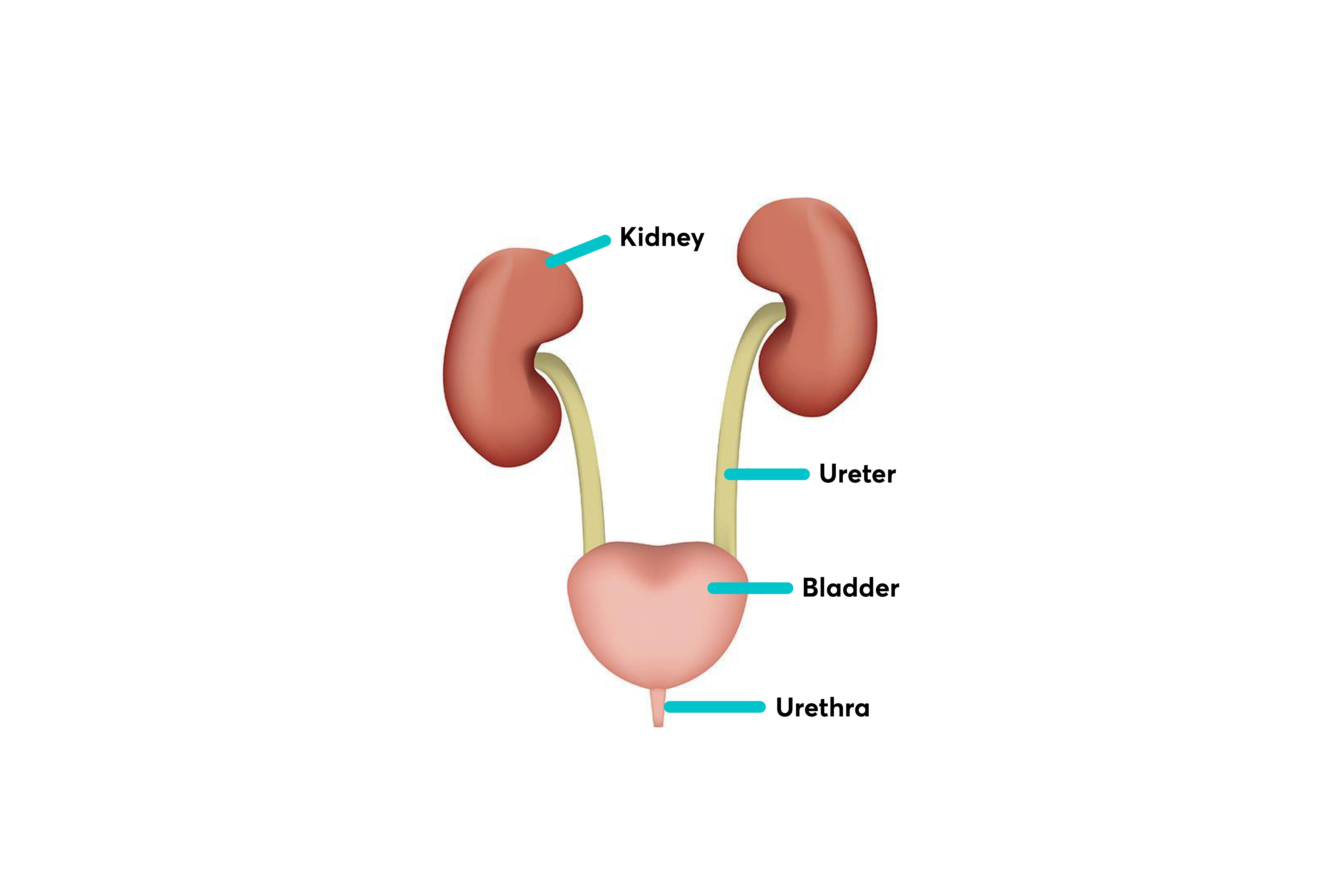
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in any part of the urinary system. This starts with the kidneys, where urine is formed. From there, urine travels through two thin tubes called ureters into the bladder before being carried out of the body via the urethra. Infections are usually caused by bacteria from poo entering the urethra and causing an infection in the bladder (cystitis). If left untreated, this can then spread to the kidneys and cause a kidney infection.
How common are UTIs?
UTIs are one of the most common types of infection in the body and account for up to 10 million GP visits each year, while UTI-related hospital admissions are thought to cost the NHS about £400m a year. UTIs are up to 30 times more common in women than men, while they are also more prevalent among the elderly and young children. Despite this, UTIs are fairly simple to both diagnose and treat, particularly when caught early.
Why are UTIs more common in women than men?
Women have much shorter urethras than men, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder and cause infections. In addition to this, the female urethra is located close to the vagina and anus, both of which are sources of germs and bacteria, meaning it’s easier for bacteria to enter the urethra. Around 50-60% of women will suffer from a UTI at least once in the course of their lifetime.
How are they treated and prevented?
Some UTIs will go away on their own but, if not, a short course of antibiotics is usually prescribed, which usually clears up symptoms within a day or two. The following are all important in preventing UTIs from returning:
- Drink plenty of water (the more you urinate, the more you flush away any bateria)
- Don’t hold it in when you need to pee!
- Keep the genital area clean
- Urinate after sex
- Wipe from front to back to avoid bacteria reaching the urethra
How can you test for UTIs?
UTIs can be detected by a simple urine sample. The Newfoundland UTI Test screens for nitrites and leukocytes in urine. Leukocytes are white blood cells - an important part of the body’s immune system - and their presence in urine indicates an infection, while nitrites are a waste product formed by bacteria, signalling an infection. The test is very simple and gives results in just two minutes. You can find them on our website, in Tesco or on Amazon.
It’s important to seek advice or treatment as soon as possible if you think you may have a UTI. Symptoms can differ depending on where the infection is, but look out for the following:
- Pain or burning sensation while urinating
- Frequent urination and/or urge to urinate
- Cloudy urine, blood in urine or strong smelling urine
- Pain or cramping in the groin or lower abdomen